Applications
Molecular Separation
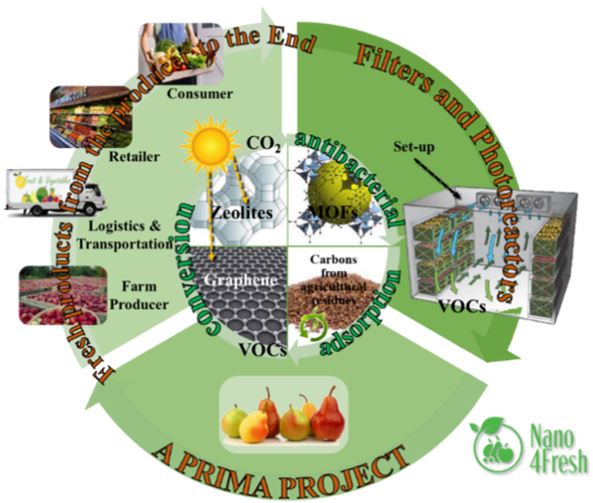
Ongoing research aims to develop advanced zeolite materials with enhanced properties and explore new applications in different research areas such as Agri-food to reduce food losses and wastes. Nano4fresh Project targets to extend the post-harvest quality and shelf-life of the fruit by removing harmful/toxic substances (e.g. ethylene inhibitors and antibacterial/antifungal) during the transport and storage period. This approach comprises the ethylene removal, from (...)
Liquid Organic Hydrogen Carriers - LOHCs
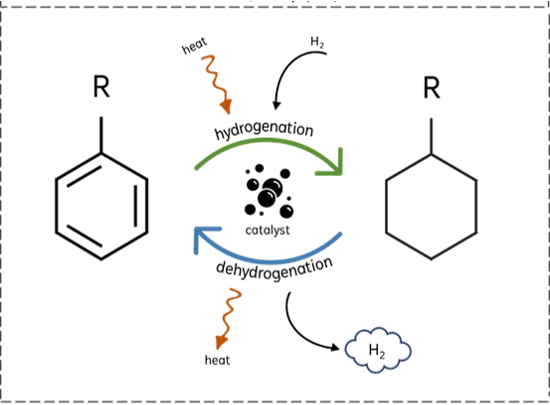
LOHCs will play a significant role in the future hydrogen economy by providing a practical and safe method for hydrogen storage, transportation, and distribution at ambient conditions. They can reversibly store and release hydrogen through hydrogenation and dehydrogenation reactions. The main challenges (...)
Carbon Capture and Utilization (CCU)
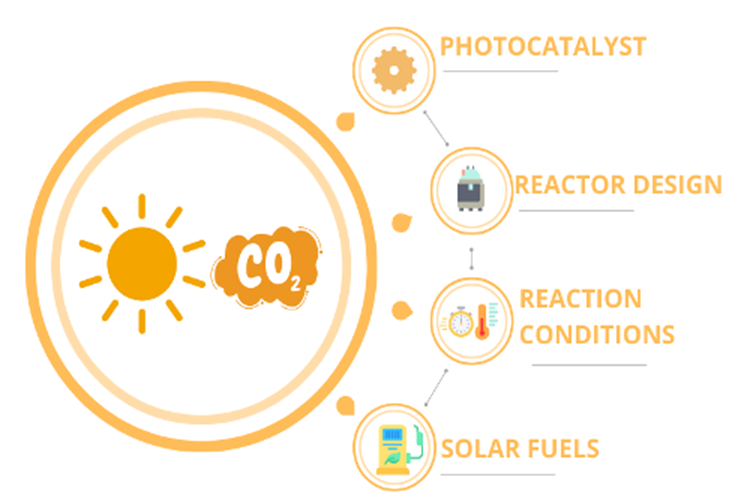
Human activity is highly dependent on fossil fuels and the burning of such emits carbon dioxide (CO2). Strategies to mitigate CO2 emissions include energy transition into renewable sources along with Carbon Capture and Utilization (CCU). Catalytic processes are being developed for CCU in where CO2 is converted into valuable products (...)
Renewable Feedstock valorization
Renewable feedstock valorization refers to the process of converting renewable raw materials or biomass into valuable products through various technological and chemical processes. This approach aims to utilize sustainable and renewable resources to produce fuels, chemicals, materials, and other valuable commodities, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing environmental impacts. A project (...)
Low-carbon Catalytic Processes
Catalytic processes play a crucial role in the transition to a more sustainable and low carbon economy. By optimizing catalyst design, reaction conditions and process efficiency, low carbon catalytic processes will help to mitigate climate change. Examples of low carbon catalytic processes: Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: Fischer-Tropsch (FT) synthesis is a catalytic process that converts carbon monoxide and hydrogen into hydrocarbon fuels, such as synthetic diesel and synthetic gasoline. It can utilize renewable sources of carbon monoxide, such as biomass or waste gases, to produce low carbon fuels. The use of carbon dioxide (CO2) as an alternative carbon source for FT synthesis (...)
Host Intitutions|Fundings|Contacts
Host Institutions | Laboratory | |||
 |  |  | ||
| Fundings | ||||
 |  |  | ||
 |